Support for Drug Development
Our Services
-
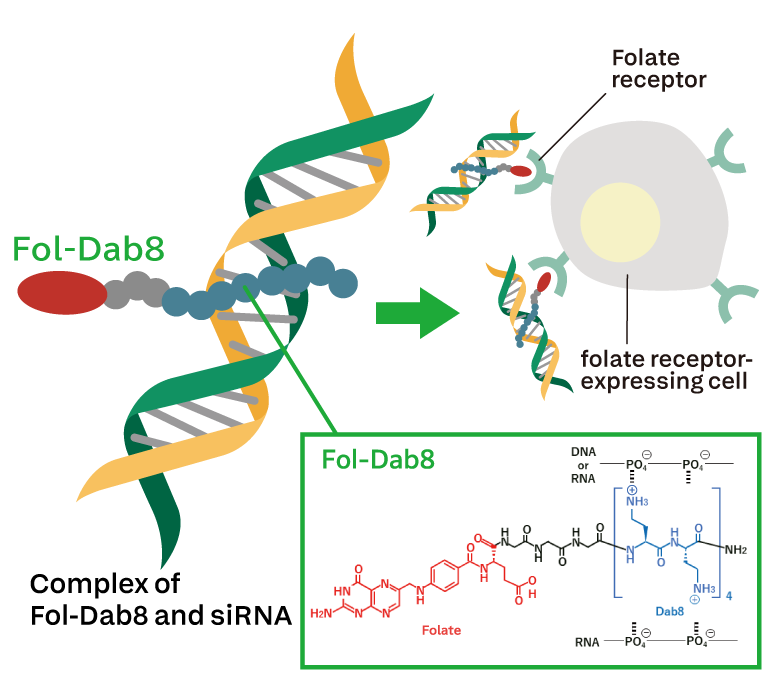
Peptides that deliver siRNA
DDS technology for selectively delivering siRNA to pancreatic cancer, etc.Fol-Dab8 is innovative DDS technology that forms a complex with siRNA and delivers siRNA to folate receptor-expressing cells (pancreatic cancer, brain tumors, breast cancer, etc.). Fol-Dab8 is available in a form of complex with siRNA of any sequence.
*This technology was co-developed with Dr. Takeshi Wada of Tokyo University of Science and Dr. Keisuke Taniuchi of Kochi University.
*Fol-Dab8 is an abbreviation for 2,4-diaminobutyric acid (Dab) octamer with folic acid (Folate) linked via a linker.

-
New biocompatible polymer(For DDS and others)
A new option following polyethylene glycol.A novel biocompatible polymer “PGLMMA” offers numerous advantages, such as being less likely to induce IgM antibody production and maintaining blood retention even after multiple doses.
*PGLMMA is an abbreviation for poly (glycerol monomethacrylate).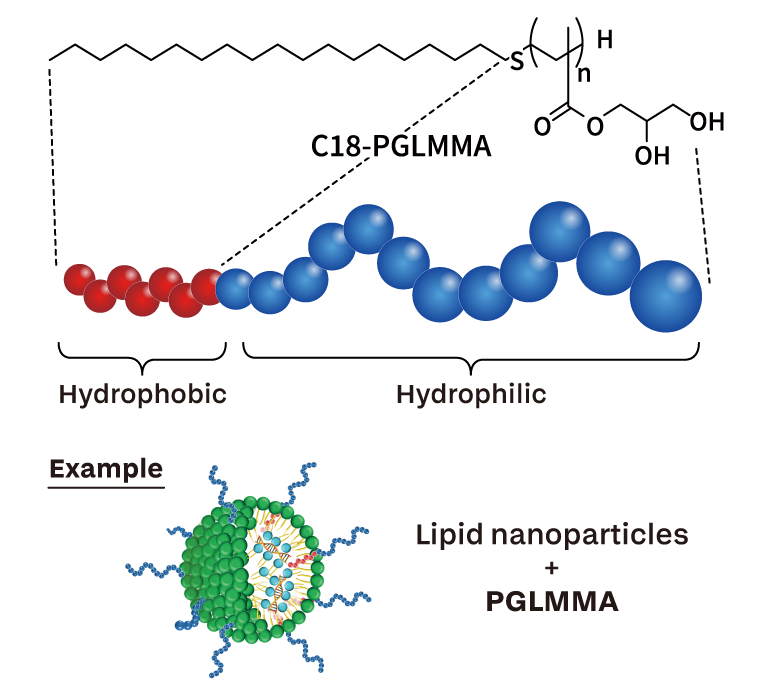
-
Heteroduplex Oligonucleotides (HDO)
Heteroduplex oligonucleotide (HDO) is the third platform technology for mRNA Therapeutics following short interfering RNA (siRNA) and single-stranded antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), which serves as a therapeutic agent for the modulation of specific genes at the post-transcriptional level. HDO is an artificial functioning nucleic acids composed of an antisense strand (gapmer, mixmer, PMO etc.) that binds to a transcript of a target gene and a carrier strand (RNA) that is complementary to the antisense strand. Since a ligand (receptor ligands, antibodies, lipids, etc.) is bound to the carrier strand, various ligands can be introduced without affecting the activity of the antisense strand enabling cell-specific delivery. HDO has high nuclear localization and low toxicity compared to ASO.


- Rena Therapeutics uses heteroduplex oligonucleotide (HDO) technology as its base technology. HDO technology was co-developed by Professor Takanori Yokota of Institute of Science Tokyo and Professor Satoshi Obika of Osaka University.
- Rena Therapeutics is a subsidiary of Nippon Shokubai.
-
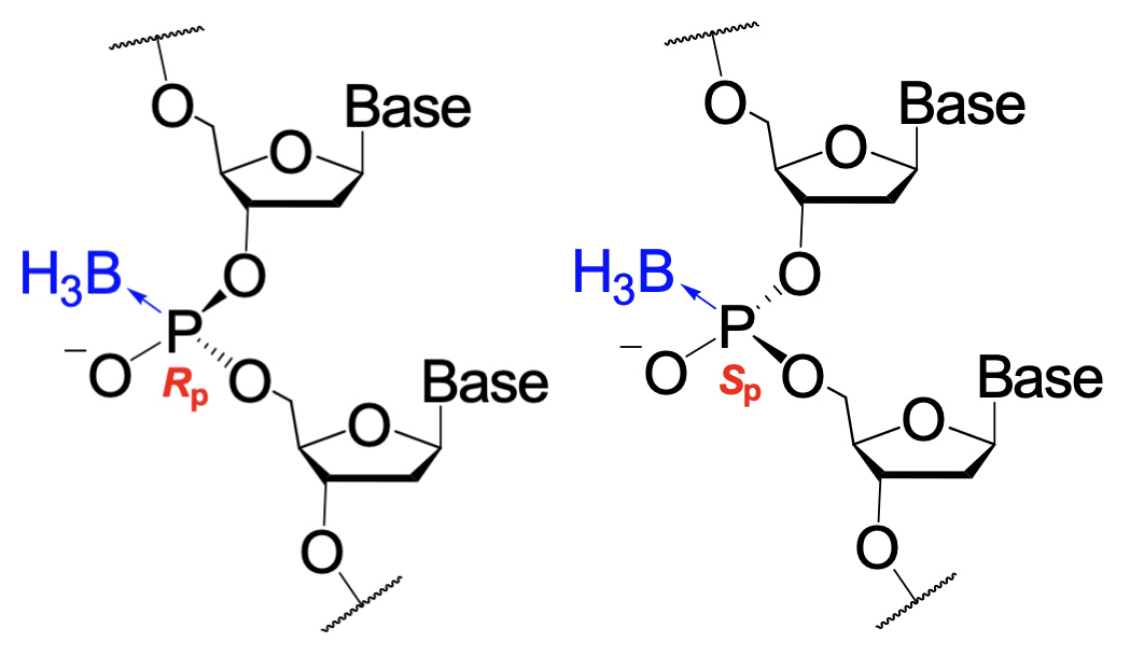
Boranophosphate Oligonucleotides
We are developing chemical synthesis techniques and practical manufacturing methods for boranophosphate oligonucleotides, which have a new structure to replace conventional phosphorothioate oligonucleotides.
-
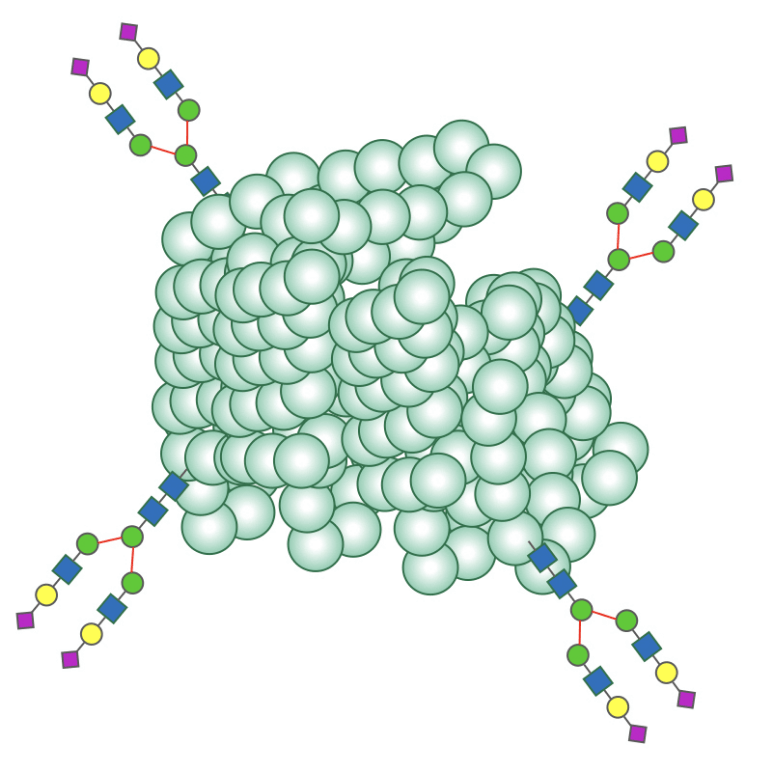
Human-type Glycan-Modified Glucocerebrosidase
This glycosylation enzyme has a uniform structure achieved by site-specific modification with human-type glycans. These changes are designed to deliver the enzyme to specific cells and intracellular organelles, and give a stable pharmacological effect. This technology is the result of joint research with GlyTech, Inc.
Glycoprotein
with fully controlled
glycan structures